-

Model Design
Transform the built 3D digital model into the walking path and extrusion amount that can be recognized by the 3D printer. First, load the model you want to print into the slicing software, and click model slicing. After slicing, send the file to the 3D printer.
-
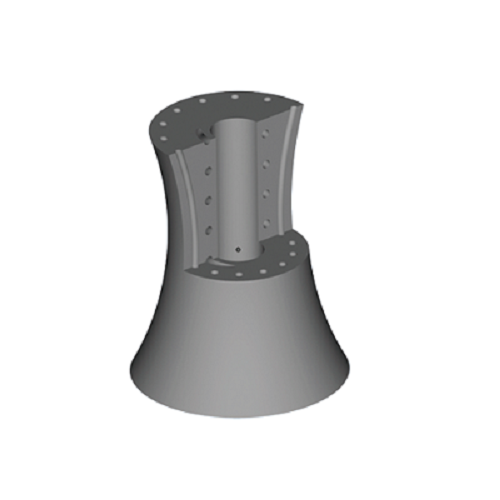
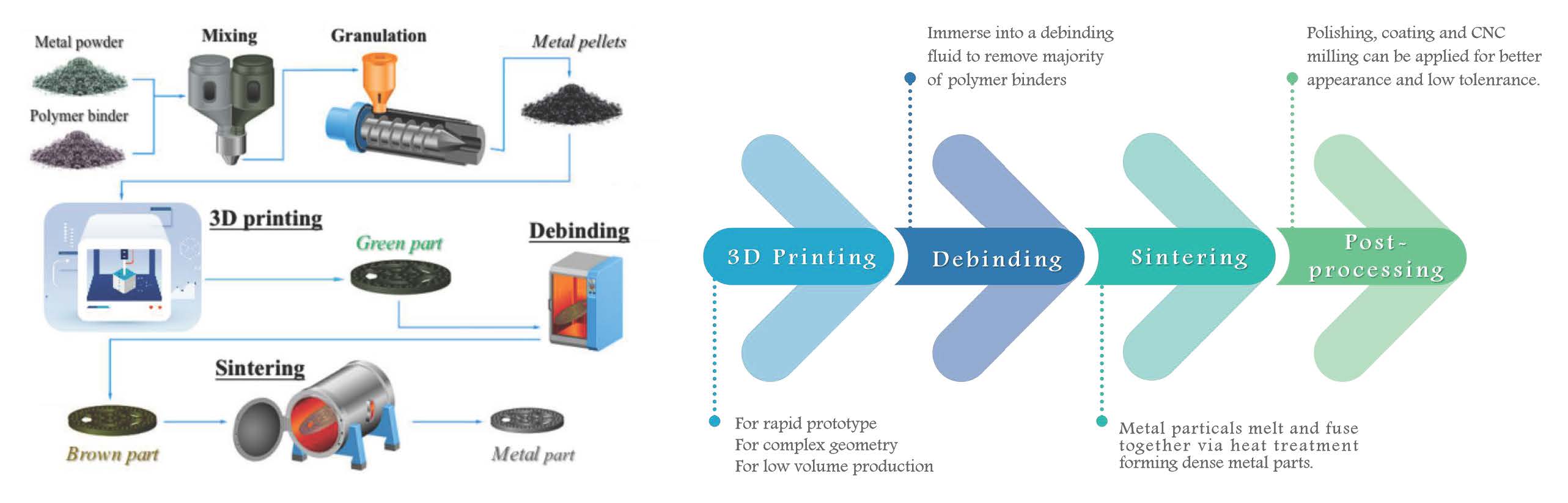
3D Printing
Based on PEP technology, metal & ceramic pellets are fused and extruded through UPRISE 3D printers, and are printed and formed layer by layer. The printed products are called "green parts", and two subsequent procedures of debinding and sintering are needed to obtain the final densified metal & ceramic products.
-
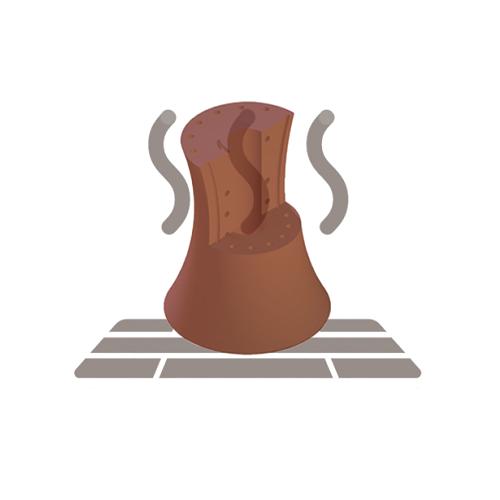

Debinding
The debinding process is to soak the printed product (green parts) in a specific solution and heat it for a certain period of time. Most of the polymer binder in the green parts produce chemical reaction with solution to produce gas and then remove it. The debinded parts are also called "brown parts".
-
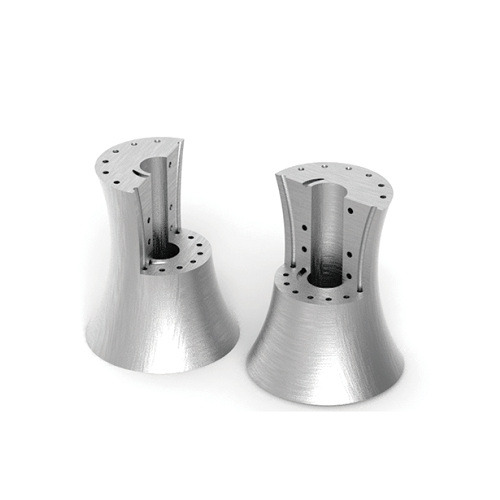

Sintering
Sintering is a process of the contraction of the manufactured parts and the final densification caused by the increase of the contact area between powder particles and the decrease of the void volume through high temperature treatment. The purpose of sintering is to adjust the properties of the parts, from porous degreasing state to non-porous material properties.
Innovative Combination of 3D Printing and Powder Metallurgy
By integrating 3D printing and traditional powder metallurgy technologies, we developed a revolutionary method, named as Power Extrusion Printing (PEP) technology. Unlike selective laser sintering (SLS) and selective laser melting (SLM), PEP technology is a revolution method, since it integrates 3D printing technology and traditional powder metallurgy industry together. 3D printing technology has maximum productivity, cost-effectiveness, outstanding flexibility and better accuracy than conventional method. Products can be printed out with designed shape.
Using 3D printing method, metals and ceramics can be printed out layer by layer with customized structure without using mold. This technology realizes a much shorter lead time as well as a much lower start-up cost.
After a green body with a certain density and strength is obtained, the product is debinded and sintered by the related process of powder injection molding technology to obtain a product with consistent and excellent performance. Powder metallurgy technology has been developed for more than 30 years, the process is mature and stable, and it is widely used in electronic 3C, automotive, medical, military, aerospace and other fields.
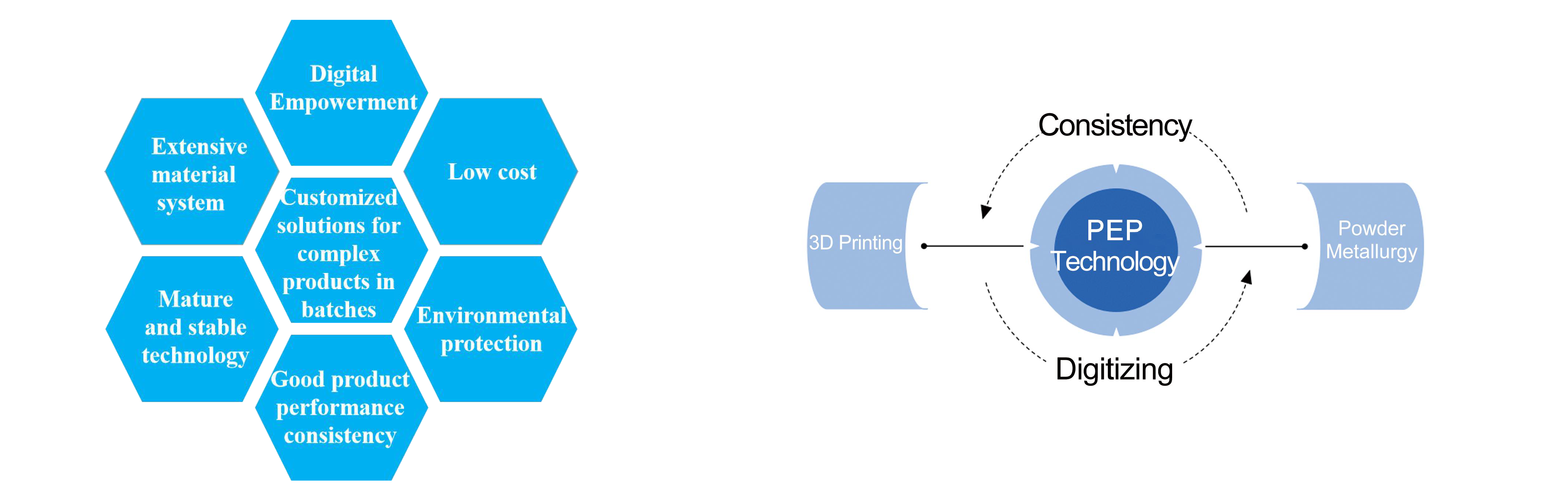
Technology Superiority
Indirect metal/ceramic 3D printing technique can drive traditional powder metallurgy towards digitalization, release more potential applications for powder metallurgy. The key benefits of this technology are listed below:
(1)Based on the well-developed powder metallurgy technology including material development, debinding and sintering process, our PEP technology is suitable for wider range of materials and can guarantee consistent performance of final sintered products.
(2)The 3D printing material system is abundant, varying from stainless steel, tungsten alloy and other metal materials; to zirconia, alumina and other ceramic materials. At the same time, we are also developing copper and copper alloy, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, etc, the almost endless list of potential materials creates favorable conditions for 3D printing to enter the application market on a large scale.
(3)Cost effective: materials can be recycled.
(4)Compared with direct 3D printing, indirect method will have larger market and higher demand because the instrument itself is relatively cheap, and can ensure excellent printing accuracy.